Network by the Numbers
Demystifying the Complexities of Network Metrics and Why They Matter to Your Enterprise
In the fast-paced world of modern business, a reliable and high-performing network isn’t just a luxury—it’s a necessity. From seamless video conferences to lightning-fast file transfers, your network’s performance can directly impact your productivity, customer satisfaction, and bottom line. However, choosing the right connectivity solution can be daunting, especially when faced with a barrage of technical jargon and complex concepts. This article aims to demystify the world of network metrics, empowering you to make informed decisions that will set your enterprise up for success.

The Hidden Language of Connectivity: Understanding Network Metrics
Behind the scenes of every online interaction lies a complex web of data transmission governed by a set of key performance indicators known as network metrics. These metrics, often shrouded in technical jargon, hold the key to unlocking your network’s true potential. Let’s break down the most important ones:
- Latency = Efficiency: Imagine latency as the time it takes for a message to travel from your computer to a server and back. Lower latency means faster response times, crucial for real-time applications like video calls and online gaming. High latency can lead to frustrating delays and disruptions.
- Throughput = Performance: This refers to the amount of data that can be transmitted over your network per unit of time. Think of it as the width of a highway – higher throughput means more data can travel simultaneously, resulting in faster downloads and uploads.
- Packet Loss = Integrity: When data travels across the network, it’s broken down into smaller units called packets. Packet loss occurs when some of these packets fail to reach their destination, leading to choppy audio, lagging video, and incomplete data transfers.
- Jitter = Variability: Even with low latency, if the arrival time of data packets varies significantly, it creates jitter. This inconsistency can disrupt real-time applications, causing audio and video quality issues.
- Uptime = Accessibility: This measures the percentage of time your network is operational. Downtime means your business is offline, leading to lost productivity and potential revenue loss.
Beyond Speed: The Metrics that Truly Matter
While download and upload speeds are often the first things people consider when choosing connectivity services, they only tell part of the story. Focusing solely on speed is like judging a car based only on its top speed, ignoring factors like handling, fuel efficiency, and safety.

Latency, packet loss, and jitter are equally important, especially for businesses that rely on real-time communication and data-intensive applications. Imagine a video conference where the audio is constantly cutting out or a critical file transfer that keeps failing due to packet loss. These issues can severely impact productivity and frustrate both employees and customers.
From Fiber to Wireless: Comparing Network Transport Types
The type of network transport used by your carrier plays a significant role in determining the overall performance and reliability of your connection. Here’s a quick comparison of the most common types:
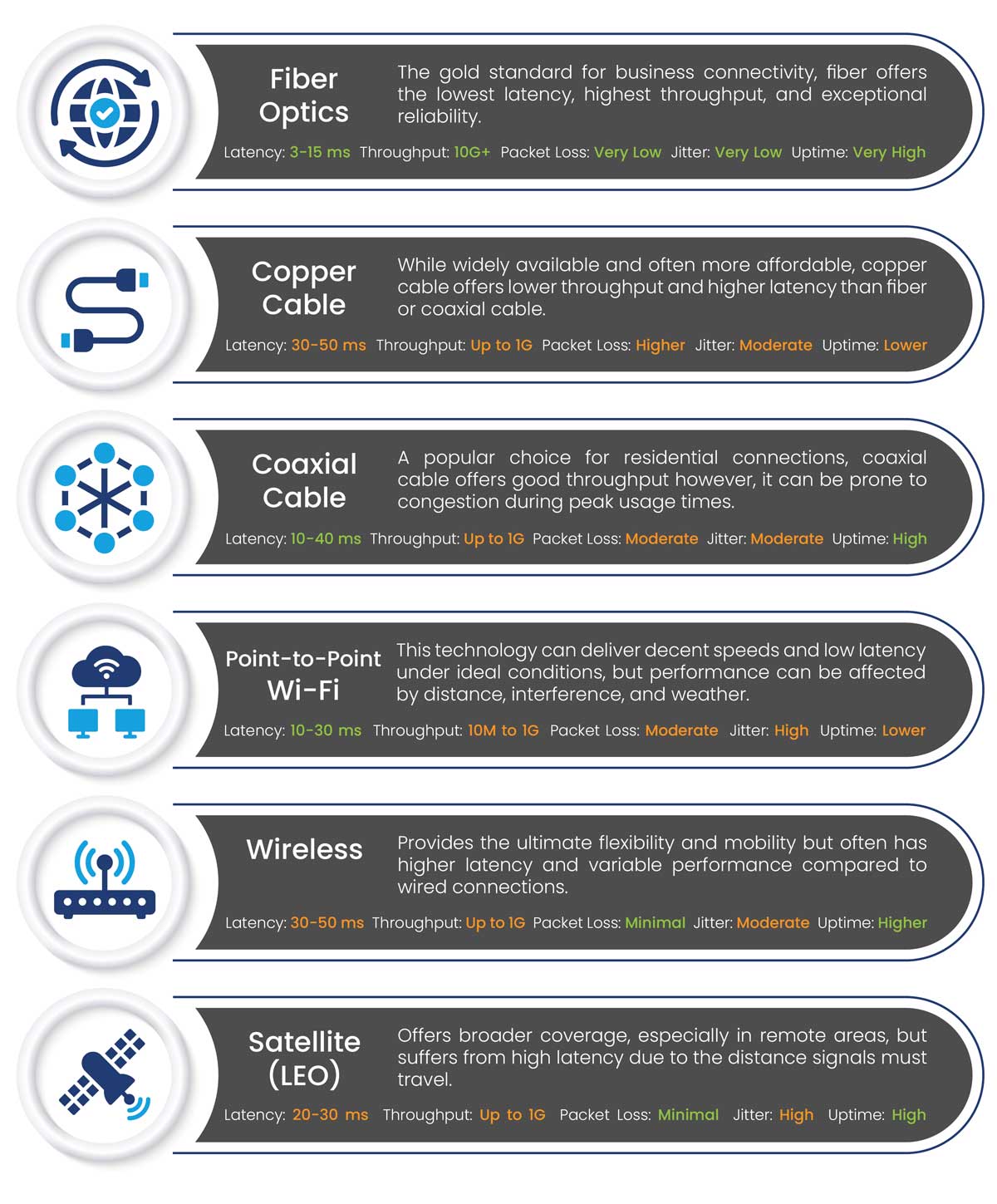
Dedicated vs. Shared: Choosing the Right Access for Your Business
When selecting an internet service, you’ll also need to decide between dedicated and shared access.
Dedicated Internet Access:
Guarantees a fixed bandwidth exclusively for your business, ensuring consistent performance even during peak usage times. This is ideal for businesses with high bandwidth demands and those that rely on real-time applications.
Shared Internet
Access:
Multiple users share the same bandwidth, which can lead to slower speeds during peak times. This option is more cost-effective but may not be suitable for businesses with critical connectivity needs.
Multi-Homed vs. Single-Homed
Multi-Homed ISP: A multi-homed ISP (Internet Service Provider) is an ISP that maintains multiple connections to the Internet, typically through two or more upstream providers or through different geographic locations. This setup enhances reliability and performance by providing redundant pathways for data to travel, reducing the likelihood of outages, and improving the overall quality of service.
Benefits of a Multi-Homed ISP:
- Redundancy: If one connection fails, traffic can be rerouted through another, minimizing downtime and service interruptions.
- Load Balancing: Traffic can be distributed across multiple connections, optimizing bandwidth usage and improving performance.
- Resilience: Enhanced ability to withstand network failures, attacks, or congestion in one part of the network without impacting overall service.
- Improved Performance: By choosing the best path for data packets, multi-homing can reduce latency and improve speed.
Single-Homed ISP: is an ISP that maintains only one connection to the Internet through a single upstream provider. This type of setup is simpler and less costly than a multi-homed configuration but comes with certain limitations in terms of redundancy and reliability.
Benefits of a Single-Homed ISP:
- Single Connection: The ISP connects to the Internet through one upstream provider, relying entirely on this connection for all Internet traffic.
- Cost-Effective: Maintaining a single connection is typically cheaper and easier to manage than multiple connections, making it a viable option for smaller ISPs or those with limited budgets.
Don’t Settle for Less: The Cost of Compromised Connectivity
In the current competitive climate, enterprises can’t afford to settle for subpar connectivity. The cost of compromised performance goes far beyond slow internet speeds. It can lead to:

Decreased Productivity: Employees waste valuable time waiting for pages to load or dealing with dropped connections.

Frustrated Customers: Slow response times and poor communication can damage your reputation and drive customers away.

Missed Opportunities: Unreliable connectivity can hinder innovation and prevent you from leveraging new technologies.
Making Informed Decisions: Tips for Choosing the Right Carrier
Choosing the carrier and connectivity solution requires careful consideration of your business needs and priorities. Here are some tips to guide your decision-making:

Assess your bandwidth needs: Consider the number of users, the types of applications you use, and your future growth plans.

Prioritize reliability and uptime: Downtime can be costly; choose a carrier with a proven track record of reliability.

Evaluate latency and jitter: If your business relies on real-time applications, prioritize low latency and jitter.

Seek expert advice: Consult with a trusted IT professional or network specialist to help you make the best decision.
Take Control of Your Connectivity
Network metrics may seem complex, but understanding them is crucial for making informed decisions about your enterprise’s connectivity. Don’t let technical jargon intimidate you. By taking the time to learn about these metrics and the different types of network transport, you can empower yourself to choose the right carrier and connectivity solution that will support your business’s growth and success.

Remember, your network is the digital backbone of your business. Make sure it’s strong, reliable, and ready to handle the demands of the modern world. If you are interested in learning more about navigating the complexities of network connectivity, don’t hesitate to reach out to experts who can guide you toward the best solution for your business.








